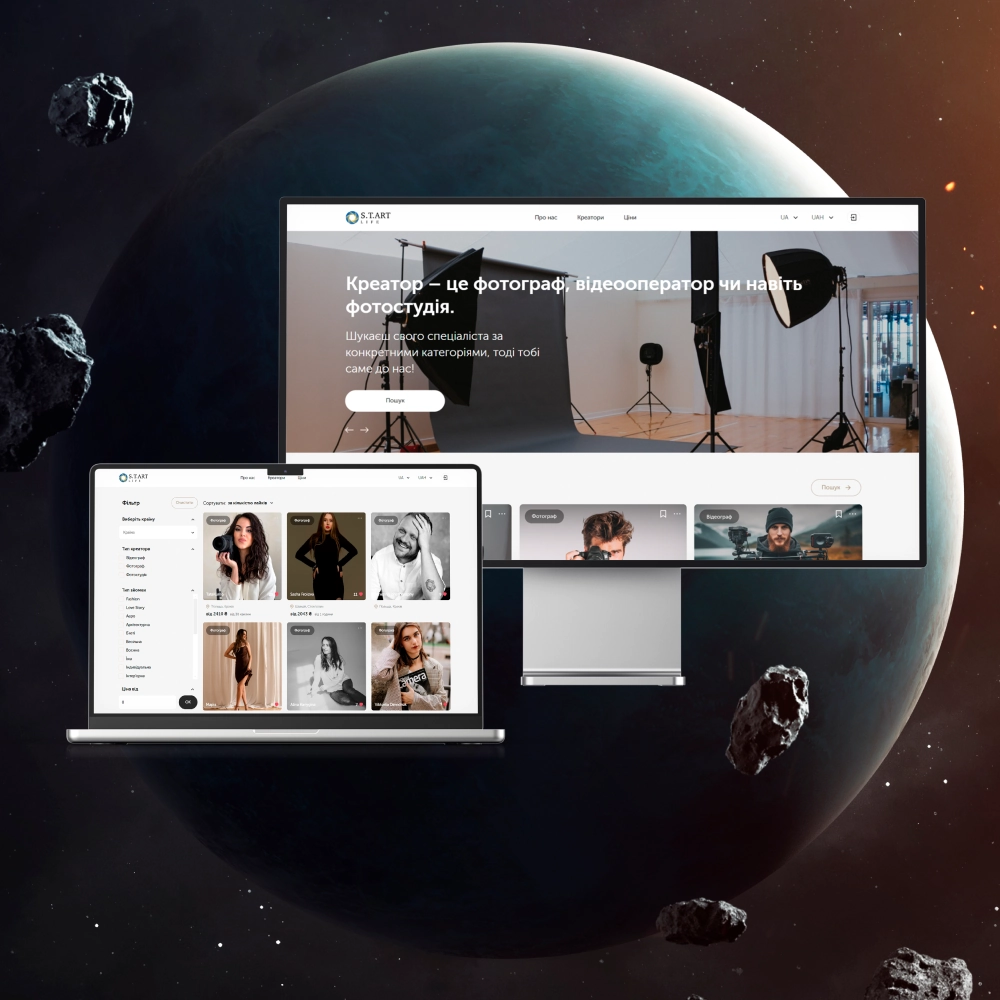
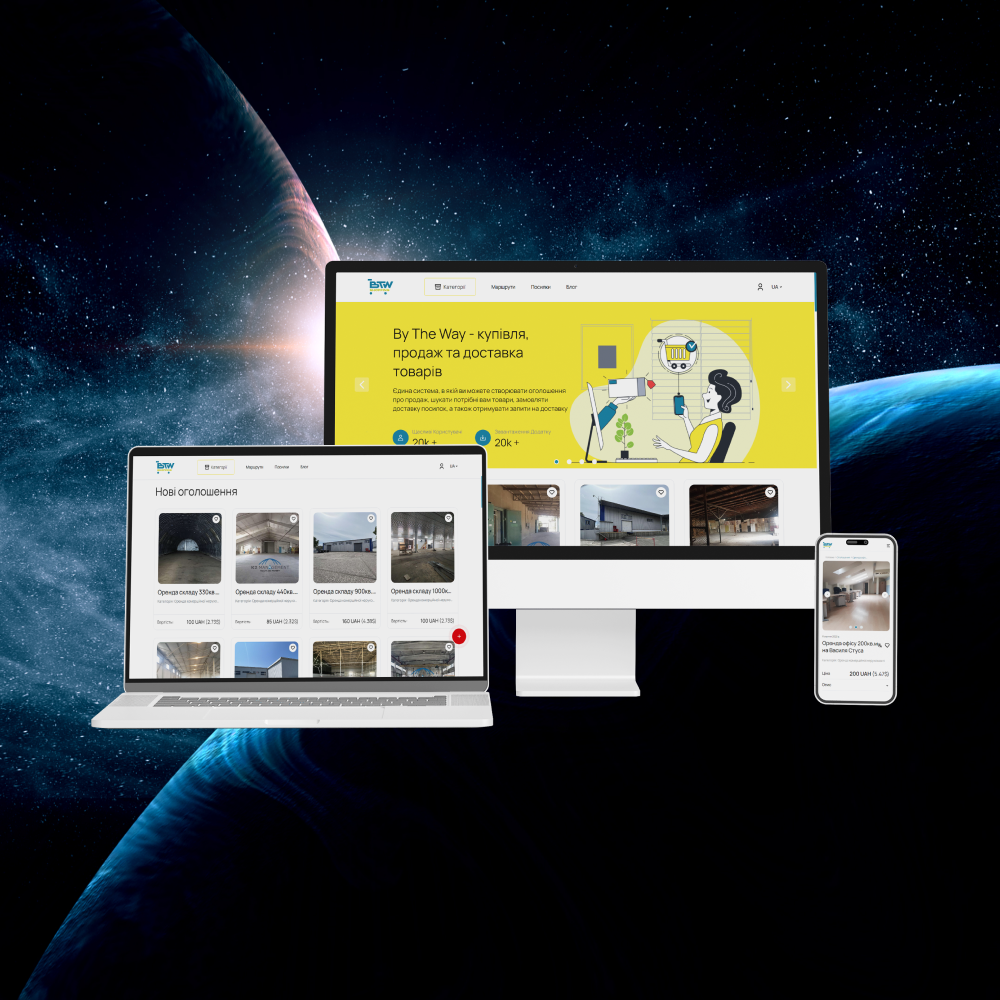
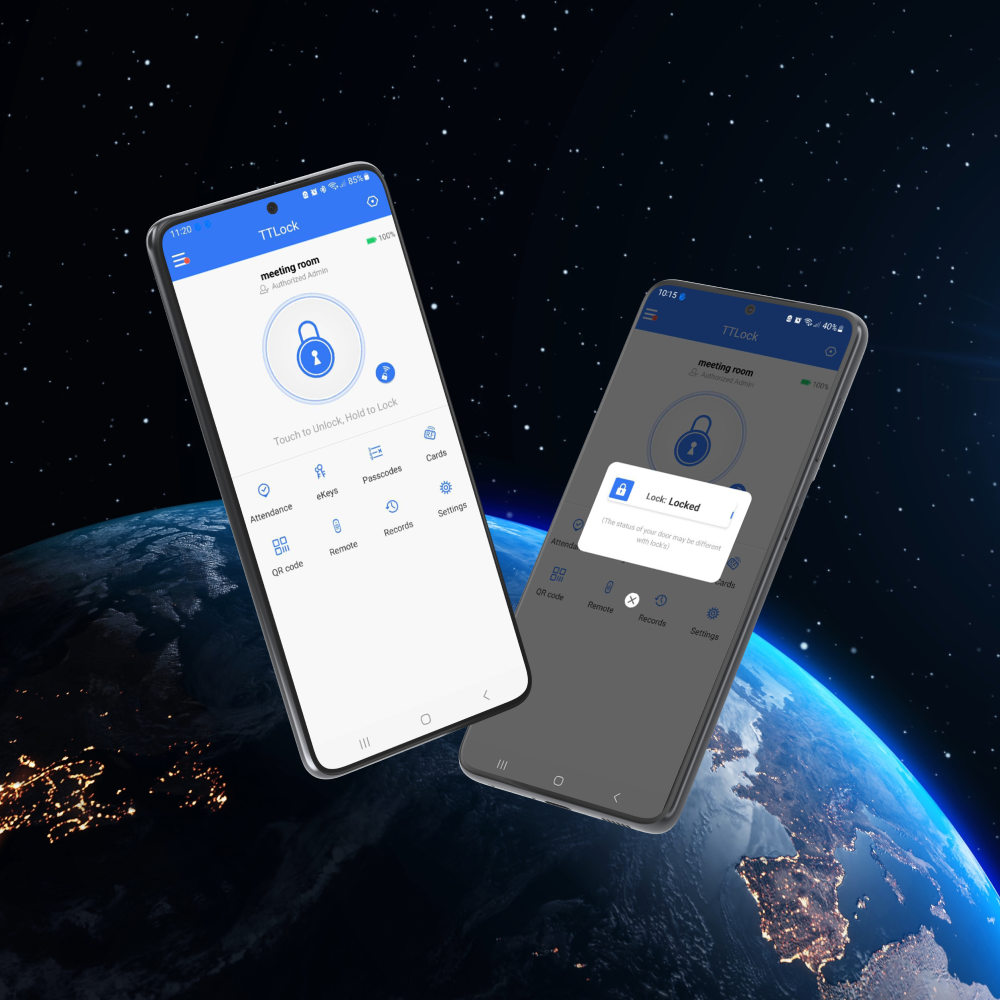
Implementation of blockchain in databases
Implementation of blockchain in databases
Professional developmentImplementation of blockchain in databases Professional development
As you know, traditional databases have limitations. The individual, business, or organization that owns the database has complete control over its structure, content, and availability, while data users are completely dependent on the integrity of the data and the owner of the database, who is often referred to as a “trustee.” And as the world becomes more connected and dependent on data and data sharing, the limitations of traditional databases pose challenges for security and trust.
These limitations have led to the development of distributed electronic database systems. It is a technology designed to democratize information by distributing and synchronizing data among multiple independent stakeholders, such as businesses or government agencies, that have chosen to participate in the system. The most common example of this system is the blockchain.
What is blockchain?
Database design and developmentWhat is blockchain? Database design and development
Introduced in 2009, blockchain is an electronic database, also called an immutable ledger. The advantage of this technology is that the blockchain adds features and functionality not found in traditional databases.
First, the blockchain system operates in a peer-to-peer (P2P) network where each node shares the computing/network load and maintains full copies of the data. As more members enter the network, the system scales to allow more records to be processed. The presence of a large number of participants in the network means greater availability and fault tolerance of the blockchain database.
Secondly, all the contents of the immutable registry (database) are linked to each other. Each entry or set of entries added to the registry is a block of data. Each block is linked to the previous block, including a cryptographic hash, timestamp, and transaction metadata.
In this way, each block is connected to form a growing “chain” of blocks to create secure and immutable records. The entry cannot be changed without changing the cryptographic hash, as well as all hashes in subsequent blocks. The combination of cryptography and the relationships between blocks makes the blockchain database very secure.
How does blockchain work?
Basic Blockchain ProcessHow does blockchain work? Basic Blockchain Process
Blockchain is most often associated with financial transactions – mostly cryptocurrency transactions like Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. As with SQL or any other database format, it can be applied to a variety of industry verticals and use cases, not just finance. Let’s take a look at the basic blockchain process:
- A transaction is requested to write a new block of data to the blockchain.
- The request is broadcast to all nodes participating in the blockchain.
- Each node participating in the blockchain checks the hashes against algorithms to confirm the transaction.
- Each node performs a sanity check process, reaches a consensus on the validity of the new block, and if the consensus succeeds, adds the block to the chain.
Encryption is at the heart of what makes a block special. Blocks are assigned a cryptographic hash generated exclusively for their data, and with the hash for the previous block.
A hash works like a fingerprint for the data: it is a sequence of hexadecimal numbers calculated using a mathematical algorithm. This algorithm creates a unique hash (fingerprint) for each block. Change one bit anywhere in the block and its hash becomes completely different. The corrected hash of this block is also transmitted and written to the subsequent block.
Blockchain Use Cases
AVADA-MEDIABlockchain Use Cases AVADA-MEDIA
A wide range of possibilities allows using blockchain technology to solve a variety of problems. Some common examples include the following:
- Finance. Financial markets are among the first to adopt blockchain, using accounting technology to replace traditional e-books, cryptocurrency payments and other market transactions and clearing.
- Administrative services. Government agencies can use blockchain to store and provide various documents: state acts, extracts from the state register, certificates, etc.
- Supply chains. Markets can use blockchain to share data, support billing, manage orders, and track the exchange of goods and services.
- Healthcare. Blockchain can be used to store and protect patient data, collect data for analytics, process medical payments, and plan and deliver medical services.
Blockchain Benefits
The latest technology used in the financial sectorBlockchain Benefits The latest technology used in the financial sector
Blockchain technology has important advantages in the field of databases, namely:
- Safety. The use of cryptography, immutability, and a distributed structure means that the blockchain database is virtually immune to hacking, fraud, and other abuse. Illegal data changes are reliably detected and rejected.
- Sustainability. Blockchain is a distributed technology: each node participating in a database uses a full copy of the database and ensures consensus in checking each node as it changes. Consensus not only improves security, but if a node goes down or is attacked, the rest of the nodes continue to function. It is extremely difficult to attack and disable every node.
- Faster operations. Since the common set of data is available to all stakeholders with access to the ledger, a blockchain database can often eliminate the traditional manual checks and transaction settlement times that accompany business transactions. This can help speed up some financial and contract business operations dramatically.
- Transparency. The complete transparency and immutability of blockchain public transactions helps to create and maintain trust in the validity and accuracy of data.
Due to globalization, as well as the fact that the number of global database thefts is increasing every year, blockchain-based databases are becoming more and more in demand.
The need for a reliable system that is immune to hacks is the catalyst for a real blockchain revolution – a technology that penetrates into all areas of human life.
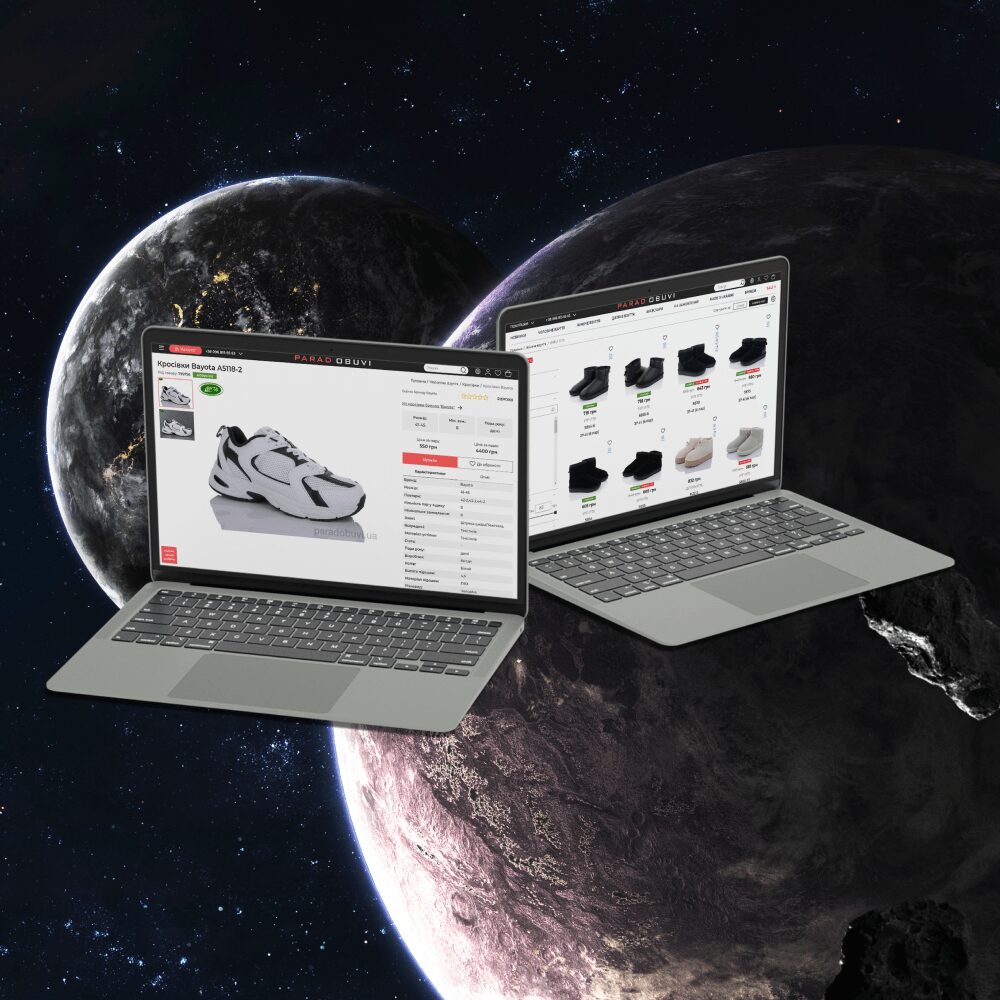
Fresh works
We create space projectsFresh works
The best confirmation of our qualifications and professionalism are the stories of the success of our clients and the differences in their business before and after working with us.
Our clients
What they say about usOur clients What they say about us
Successful projects are created only by the team
Our teamSuccessful projects
are created only by the team Our team












Contact the experts
Have a question?Contact the experts Have a question?
-
Phone:+ 38 (097) 036 29 32
-
E-mail:info@avada-media.com.ua